Abstract
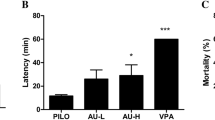
Abnormal and sometimes severe behavioral and molecular symptoms are usually observed in epileptic humans and animals. To address this issue, we examined the behavioral and molecular aspects of seizure evoked by pilocarpine. Autophagy can promote both cell survival and death, but there are controversial reports about the neuroprotective or neurodegenerative effects of autophagy in seizure. Cannabidiol has anticonvulsant properties in some animal models when used as a pretreatment. In this study, we investigated alteration of seizure scores, autophagy pathway proteins, and antioxidant status in hippocampal cells during the chronic phase of pilocarpine-induced epilepsy after treatment with cannabidiol. Cannabidiol (100 ng, intracerebroventricular injection) delayed the chronic phase of epilepsy. Single administration of cannabidiol during the chronic phase of seizure significantly diminished seizure scores such as mouth clonus, head nodding, monolateral and bilateral forelimb clonus and increased the activity of catalase enzyme and reduced glutathione content. Such a protective effect in the behavioral scores of epileptic rats was also observed after repeated administrations of cannabidiol at the onset of the silent phase. Moreover, the amount of Atg7, conjugation of Atg5/12, Atg12, and LC3II/LC3I ratio increased significantly in epileptic rats treated with repeated injections of cannabidiol. In short, our results suggest that post-treatment of Cannabidiol could enhance the induction of autophagy pathway and antioxidant defense in the chronic phase of epilepsy, which could be considered as the protective mechanisms of cannabidiol in a temporal lobe epilepsy model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Arida RM, Scorza FA, Peres CA, Cavalheiro EA (1999) The course of untreated seizures in the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 34:99–107
Bartolomei F, Khalil M, Wendling F et al (2005) Entorhinal cortex involvement in human mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: an electrophysiologic and volumetric study. Epilepsia 46:677–687
Benz AP, Niquet J, Guy Wasterlain C, Rami A (2014) Status epilepticus in the immature rodent brain alters the dynamics of autophagy. Curr Neurovasc Res 11:125–135
Berger Z, Davies JE, Luo S et al (2006) Deleterious and protective properties of an aggregate-prone protein with a polyalanine expansion. Hum Mol Genet 15:453–465
Bisogno T, Hanus L, De Petrocellis L et al (2001) Molecular targets for cannabidiol and its synthetic analogues: effect on vanilloid VR1 receptors and on the cellular uptake and enzymatic hydrolysis of anandamide. Br J Pharmacol 134:845–852
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Burstein S (2015) Cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogs: a review of their effects on inflammation. Bioorg Med Chem 23:1377–1385
Cao L, Chen R, Xu J, Lin Y, Wang R, Chi Z (2009) Vitamin E inhibits activated chaperone-mediated autophagy in rats with status epilepticus. Neuroscience 161:73–77
Carrier EJ, Auchampach JA, Hillard CJ (2006) Inhibition of an equilibrative nucleoside transporter by cannabidiol: a mechanism of cannabinoid immunosuppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:7895–7900
Castillo A, Tolón MR, Fernández-Ruiz J, Romero J, Martinez-Orgado J (2010) The neuroprotective effect of cannabidiol in an in vitro model of newborn hypoxic–ischemic brain damage in mice is mediated by CB2 and adenosine receptors. Neurobiol Dis 37:434–440
Cavalheiro EA (1995) The pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Ital J Neurol Sci 16:33–37
Chiurchiù V, Lanuti M, De Bardi M, Battistini L, Maccarrone M (2014) The differential characterization of GPR55 receptor in human peripheral blood reveals a distinctive expression in monocytes and NK cells and a proinflammatory role in these innate cells. Int Immunol 27(3):153–160. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxu097
Consroe P, Wolkin A (1977) Cannabidiol—antiepileptic drug comparisons and interactions in experimentally induced seizures in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 201:26–32
Dong Y, Wang S, Zhang T et al (2013) Ascorbic acid ameliorates seizures and brain damage in rats through inhibiting autophagy. Brain Res 1535:115–123
Eftekhari S, Mehrabi S, Soleimani M et al (2014) bDNF modifies hippocampal KCC2 and NKCC1 expression in a temporal lobe epilepsy model. Acta Neurobiol Exp 74:276–287
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Engel J (2001) Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: what have we learned? Neuroscientist 7:340–352
Fernandez-Ruiz J, Sagredo O, Pazos MR et al (2013) Cannabidiol for neurodegenerative disorders: important new clinical applications for this phytocannabinoid? Br J Clin Pharmacol 75:323–333
Freitas RM, Vasconcelos SM, Souza FC, Viana GS, Fonteles MM (2005) Oxidative stress in the hippocampus after pilocarpine‐induced status epilepticus in Wistar rats. FEBS J 272:1307–1312
Garcia-Arencibia M, Gonzalez S, de Lago E, Ramos JA, Mechoulam R, Fernandez-Ruiz J (2007) Evaluation of the neuroprotective effect of cannabinoids in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease: importance of antioxidant and cannabinoid receptor-independent properties. Brain Res 1134:162–170
Gordon E, Devinsky O (2001) Alcohol and marijuana: effects on epilepsy and use by patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 42:1266–1272
Gupta RC, Milatovic D, Dettbarn W-D (2001) Depletion of energy metabolites following acetylcholinesterase inhibitor-induced status epilepticus: protection by antioxidants. Neurotoxicology 22:271–282
Hara T, Nakamura K, Matsui M et al (2006) Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature 441:885–889
Hochfeld WE, Lee S, Rubinsztein DC (2013) Therapeutic induction of autophagy to modulate neurodegenerative disease progression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:600–604
Iuvone T, Esposito G, Esposito R, Santamaria R, Di Rosa M, Izzo AA (2004) Neuroprotective effect of cannabidiol, a non-psychoactive component from Cannabis sativa, on beta-amyloid-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 89:134–141
Iuvone T, Esposito G, De Filippis D, Scuderi C, Steardo L (2009) Cannabidiol: a promising drug for neurodegenerative disorders? CNS Neurosci Ther 15:65–75
Jones NA, Hill AJ, Smith I et al (2010) Cannabidiol displays antiepileptiform and antiseizure properties in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 332:569–577
Jones NA, Glyn SE, Akiyama S et al (2012) Cannabidiol exerts anti-convulsant effects in animal models of temporal lobe and partial seizures. Seizure 21:344–352
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T et al (2000) LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J 19:5720–5728
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T et al (2006) Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature 441:880–884
Kozela E, Pietr M, Juknat A, Rimmerman N, Levy R, Vogel Z (2010) Cannabinoids Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol differentially inhibit the lipopolysaccharide-activated NF-κB and interferon-β/STAT proinflammatory pathways in BV-2 microglial cells. J Biol Chem 285:1616–1626
Levine B, Klionsky DJ (2004) Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell 6:463–477
Liput DJ, Hammell DC, Stinchcomb AL, Nixon K (2013) Transdermal delivery of cannabidiol attenuates binge alcohol-induced neurodegeneration in a rodent model of an alcohol use disorder. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 111:120–127
Ludanyi A, Eross L, Czirjak S et al (2008) Downregulation of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor and related molecular elements of the endocannabinoid system in epileptic human hippocampus. J Neurosci 28:2976–2990
Maione S, Piscitelli F, Gatta L et al (2011) Non-psychoactive cannabinoids modulate the descending pathway of antinociception in anaesthetized rats through several mechanisms of action. Br J Pharmacol 162:584–596
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A, Kroemer G (2007) Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:741–752
Meijer AJ (2003) Amino acids as regulators and components of nonproteinogenic pathways. J Nutr 133:2057S–2062S
Momeni P, Schymick J, Jain S et al (2006) Analysis of IFT74 as a candidate gene for chromosome 9p-linked ALS-FTD. BMC Neurol 6:44
Monory K, Massa F, Egertová M et al (2006) The endocannabinoid system controls key epileptogenic circuits in the hippocampus. Neuron 51:455–466
Murillo-Rodriguez E, Millan- Aldaco D, Palomero- Rivero M, Mechoulam R, Drucker- Colin R (2006) Cannabidiol, a constituent of Cannabis sativa, modulates sleep in rats. FEBS Lett 580:4337–4345
O’Sullivan SE, Sun Y, Bennett AJ, Randall MD, Kendall DA (2009) Time-dependent vascular actions of cannabidiol in the rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol 612:61–68
Otabe H, Nibuya M, Shimazaki K et al (2014) Electroconvulsive seizures enhance autophagy signaling in rat hippocampus. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 50:37–43
Paxinos G, Watson CR (2007). The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego
Pestana RR, Kinjo ER, Hernandes MS, Britto LR (2010) Reactive oxygen species generated by NADPH oxidase are involved in neurodegeneration in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci Lett 484:187–191
Puffenbarger RA, Boothe AC, Cabral GA (2000) Cannabinoids inhibit LPS‐inducible cytokine mRNA expression in rat microglial cells. Glia 29:58–69
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:281–294
Rubinsztein DC, Gestwicki JE, Murphy LO, Klionsky DJ (2007) Potential therapeutic applications of autophagy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:304–312
Ryan D, Drysdale AJ, Lafourcade C, Pertwee RG, Platt B (2009) Cannabidiol targets mitochondria to regulate intracellular Ca2+ levels. J Neurosci 29:2053–2063
Schiavon AP, Bonato JM, Milani H, Guimarães FS, de Oliveira RMW (2015) Influence of single and repeated cannabidiol administration on emotional behavior and markers of cell proliferation and neurogenesis in non-stressed mice. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 64:27–34. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.06.017
Scuderi C, Filippis DD, Iuvone T, Blasio A, Steardo A, Esposito G (2009) Cannabidiol in medicine: a review of its therapeutic potential in CNS disorders. Phytother Res 23:597–602
Shirazi-zand Z, Ahmad-Molaei L, Motamedi F, Naderi N (2013) The role of potassium BK channels in anticonvulsant effect of cannabidiol in pentylenetetrazole and maximal electroshock models of seizure in mice. Epilepsy Behav 28:1–7
Tejada S, Sureda A, Roca C, Gamundi A, Esteban S (2007) Antioxidant response and oxidative damage in brain cortex after high dose of pilocarpine. Brain Res Bull 71:372–375
Underwood BR, Imarisio S, Fleming A et al (2010) Antioxidants can inhibit basal autophagy and enhance neurodegeneration in models of polyglutamine disease. Hum Mol Genet 19:3413–3429
Voutsinos-Porche B, Koning E, Clément Y et al (2006) EAAC1 glutamate transporter expression in the rat lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1419–1430
Wallace MJ, Martin BR, DeLorenzo RJ (2002) Evidence for a physiological role of endocannabinoids in the modulation of seizure threshold and severity. Eur J Pharmacol 452:295–301
Winslow AR, Rubinsztein DC (2008) Autophagy in neurodegeneration and development. Biochim Biophys Acta 1782:723–729, Molecular Basis of Disease
Zare N, Khalifeh S, Khodagholi F, Shahamati SZ, Motamedi F, Maghsoudi N (2015) Geldanamycin reduces Aβ-associated anxiety and depression, concurrent with autophagy provocation. J Mol Neurosci 57:317–324
Acknowledgments
This work is part of the PhD student thesis of M. Hosseinzadeh at the Neuroscience Research Center of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinzadeh, M., Nikseresht, S., Khodagholi, F. et al. Cannabidiol Post-Treatment Alleviates Rat Epileptic-Related Behaviors and Activates Hippocampal Cell Autophagy Pathway Along with Antioxidant Defense in Chronic Phase of Pilocarpine-Induced Seizure. J Mol Neurosci 58, 432–440 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0703-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0703-6